Saunas
Definition
- A sauna is a cabin or enclosed area incorporating a heater with diabase or peridotite rocks to provide a dry air temperature of between 70°C and 95°C.
- The relative humidity varies between about 5 and 30% depending upon whether water has been ladled on to the stones.
Wall and Ceilings
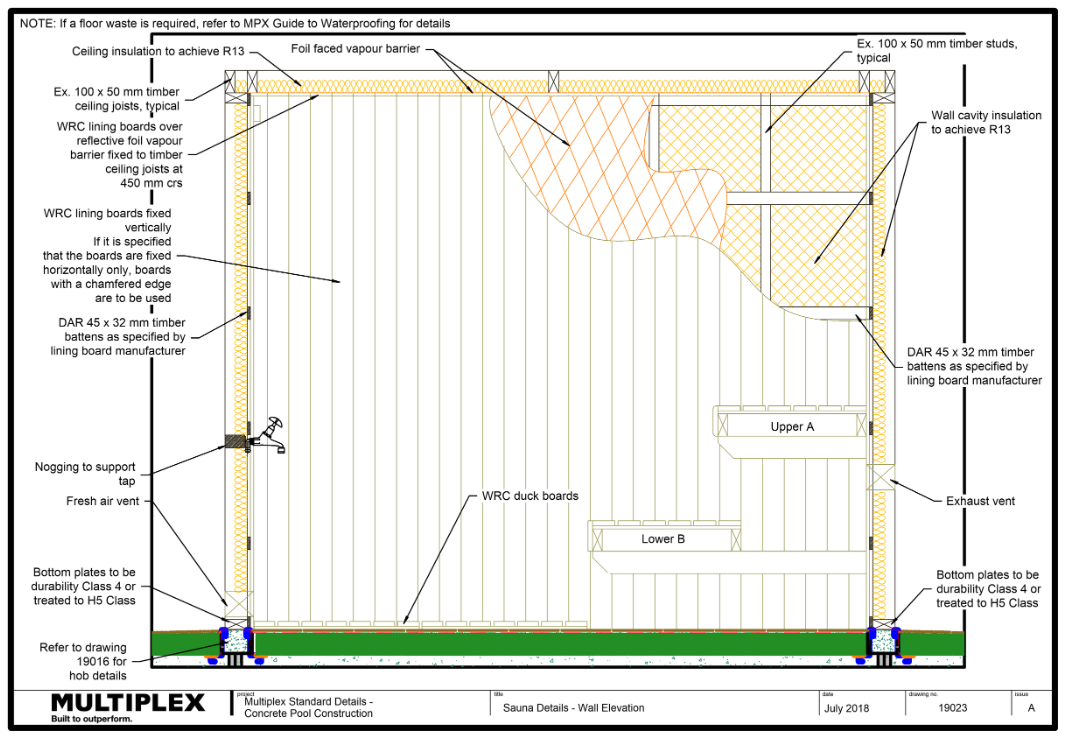
- Saunas must have wall and ceiling framing made of solid timber.
- Softwood species are preferred over hardwoods.
- Timber must not contain sapwood.
- Bottom plates must be to be durability Class 2[1] or treated to H4[2] Class.
- Studs must be a minimum of Class 3[3] or treated to H3[4].
- Thickness of the walls and ceiling should be not less than 100 mm – including internal:
- Cladding
- Insulation.
- The wall and ceiling system must achieve a minimum of R13.
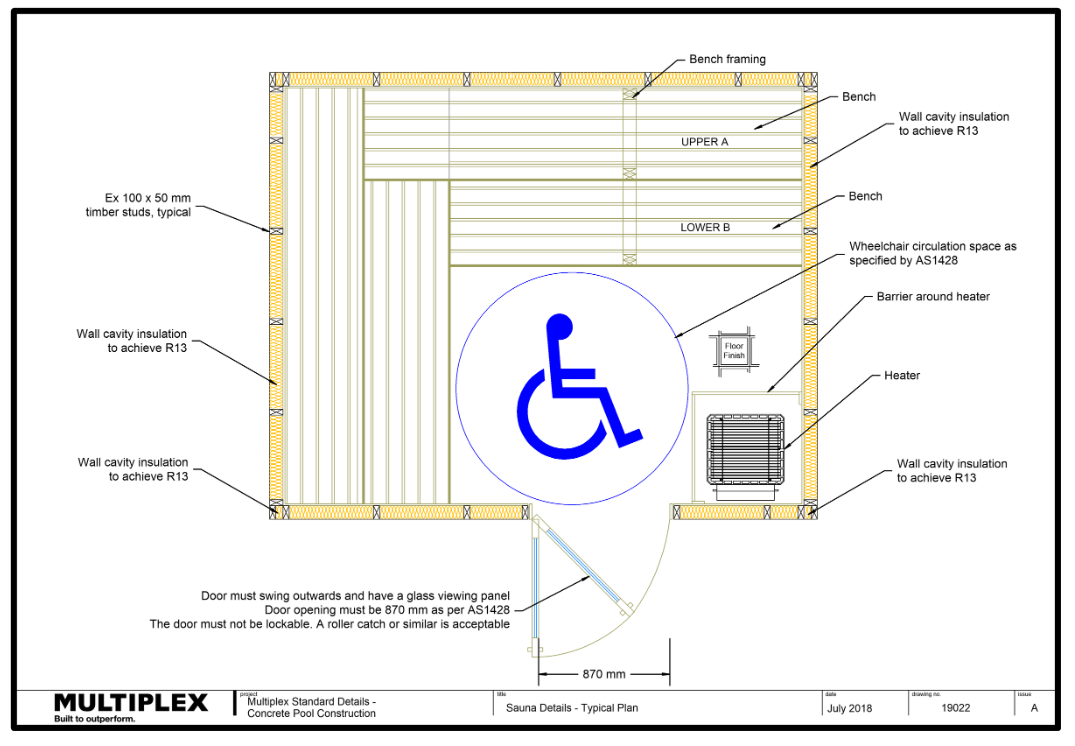
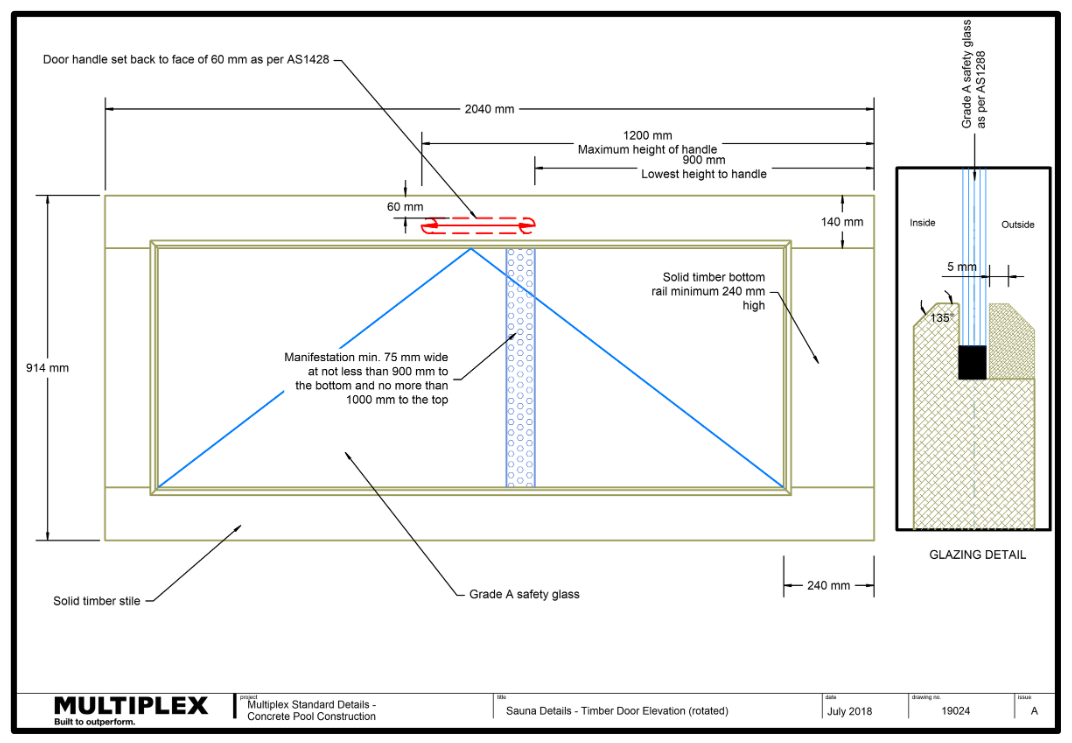
Doors
Internal Benches
- Benches must be constructed using timber:
- Free from large and or loose knots
- Free from splits and shakes
- Planed and smooth-sanded
- With all edges rounded.
- Timbers such as western red cedar, aspen or obeche are ideal for this purpose.
- Bench slats should be free from resin.
Ventilation
- All saunas must be:
- Provided with a high-level outlet and a low-level inlet vent controlled by a sliding wooden shutter from within the sauna.
- Positioned to provide good cross circulation of air.
Sauna Heaters
- Sauna heaters:
- Must be capable of producing a maximum sauna room temperature of 100°C within a heat up period of 60 minutes allowing a reasonable ambient air temperature.
- Should be protected by a stout timber guardrail fitted in such a way as to protect bathers from accidental contact with any part of the hot heater or rocks.
Flooring
The sauna floor must be anti-slip, using non-porous suitable tiles, or another suitable floor covering.
Document Control
Version 01 October 2021